Thyroid Disease: An Overview
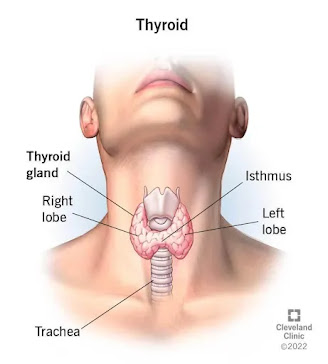
The thyroid gland, a tiny organ with the shape of a butterfly that is situated in the neck, is prone to the frequent disease known as thyroid disease. The thyroid gland creates hormones that control metabolism—the pace at which the body burns through energy. Hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism are both conditions that can result from the thyroid gland not working properly (an overactive thyroid).
Thyroid Disease Signs and Symptoms
Depending on whether the thyroid gland is hyperactive or underactive, thyroid illness symptoms might change. Fatigue, weight gain, aversion to the cold, aches in the muscles and joints, and sadness are all common signs of hypothyroidism. While anxiety, irritability, and a rapid or erratic heartbeat are typical signs of hyperthyroidism, so too are weight loss and an increased appetite.
What Causes Thyroid Disease?
Although the causes of thyroid disease can vary, some of the more frequent ones are autoimmune conditions, radiation therapy, and surgical thyroid gland removal. Hypothyroidism can result from autoimmune diseases that induce the immune system to assault the thyroid gland, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Hypothyroidism can result from thyroid damage caused by radiation therapy for diseases like cancer. Last but not least, hypothyroidism can also develop from surgical removal of the thyroid gland.
Diagnosis of Thyroid Disease
A physical exam and a review of your medical history are frequently the first steps in the diagnosis of thyroid illness. Your doctor may also request blood tests to examine your hormone levels and search for antibodies that could signify an autoimmune condition. To confirm a diagnosis, it may occasionally be necessary to perform a thyroid gland biopsy.
Treatment of Thyroid Disease
The type of thyroid illness you have and the degree of your symptoms will determine how your condition is treated. Treatment for hypothyroidism often entails taking a daily hormone replacement supplement, such as levothyroxine, to make up for the hormones your thyroid gland isn't making. Antithyroid drugs, radioactive iodine, and thyroid gland removal surgery are all possible treatments for hyperthyroidism.
Living With A Thyroid Condition
Living with thyroid disease can be difficult, but most individuals are able to lead healthy, active lives with the right management and medication. Working closely with your healthcare practitioner will help you keep an eye on your condition and change your treatment plan as necessary. You can manage your symptoms and enhance your general health by engaging in regular exercise and eating a balanced diet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, successful management and therapy of thyroid disease depend on an understanding of the condition. It is crucial to see a healthcare professional for an accurate assessment and diagnosis if you are exhibiting thyroid disease symptoms. Most thyroid disease sufferers can have active, healthy lives with the correct medicine and lifestyle changes.










0 comments:
Post a Comment